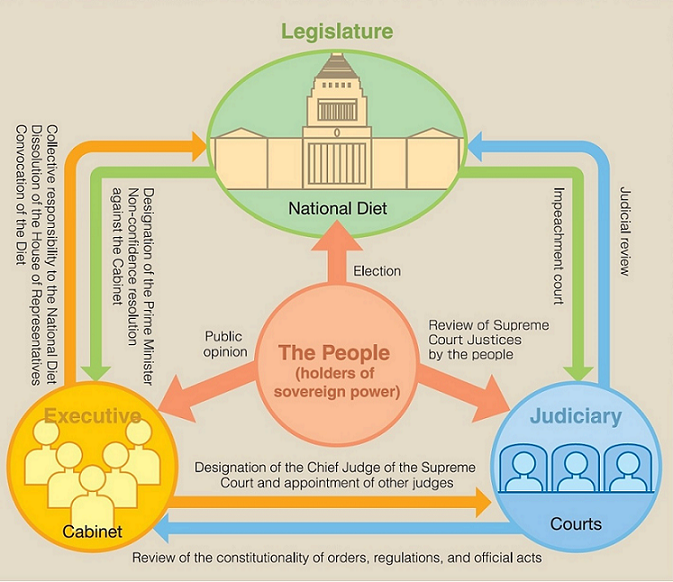
Separation of Powers
The Constitution of Japan provides for the principle of the separation of powers. Three independent organs — the Diet, the Cabinet, and the Judiciary — are established, and each limits the power of the others through a system of checks and balances. This prevents the abuse of power and guarantees the rights and freedom of the people.